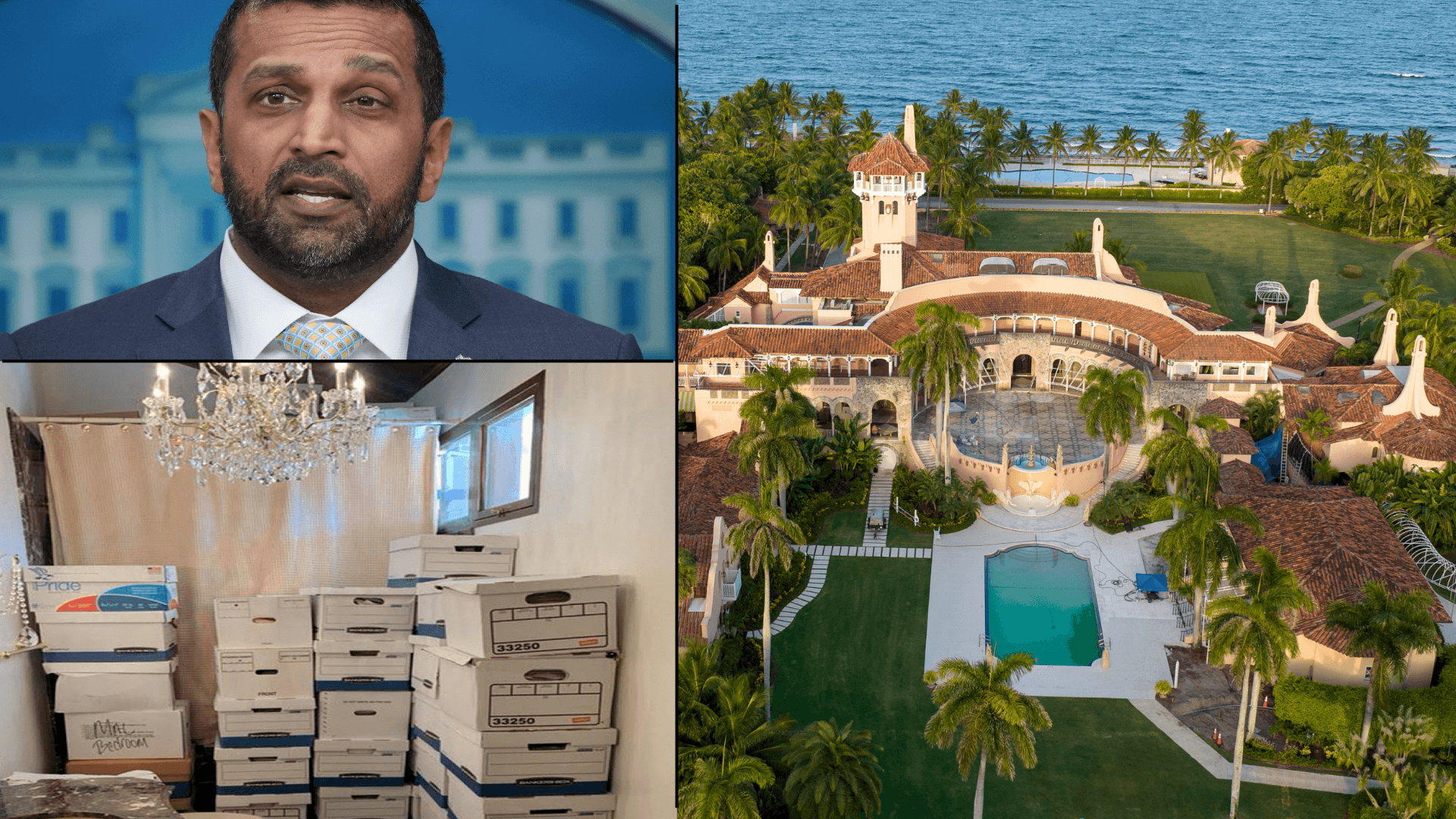
Exclusive: FBI Staffers Fired for Role in Mar-a-Lago Probe Were Assigned to Espionage Unit That Investigated Iranian Threats in America, Sources Say
By DANIEL EDWARD ROSEN
|This article is from the archive of The New York Sun before the launch of its new website in 2022. The Sun has neither altered nor updated such articles but will seek to correct any errors, mis-categorizations or other problems introduced during transfer.

Already have a subscription? Sign in to continue reading

By DANIEL EDWARD ROSEN
|
By A.R. HOFFMAN
|
$0.01/day for 60 days
Cancel anytime
By continuing you agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service.
By HOLLIE McKAY
|